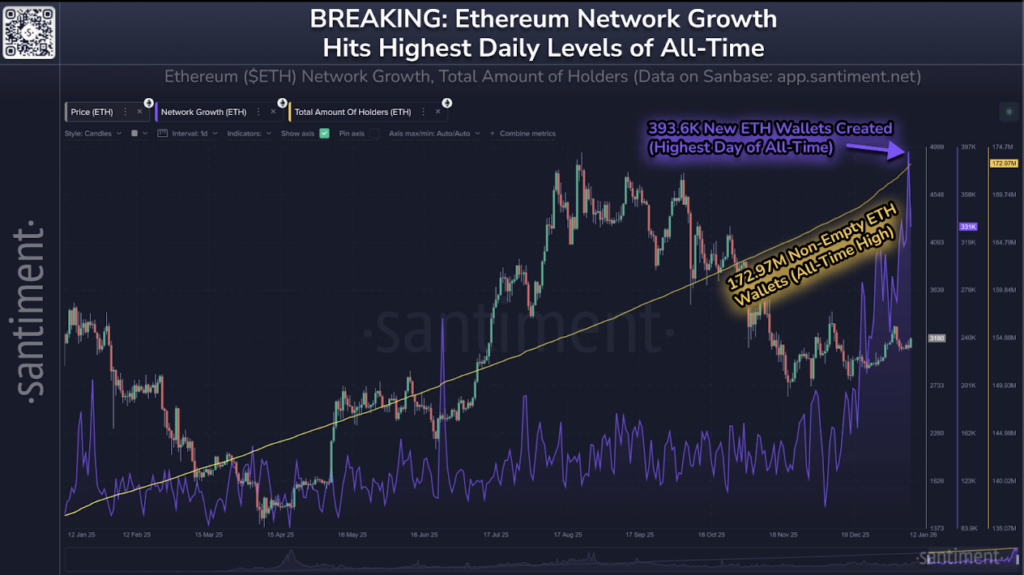
- Ethereum’s recent surge in network activity may be partly driven by address poisoning attacks enabled by lower gas fees
- On-chain data shows millions of new wallets receiving dust transactions, inflating activity metrics and increasing user risk
- Technical indicators remain bearish, suggesting price strength has yet to confirm the spike in network usage
Ethereum’s recent spike in network activity has sparked a familiar debate across the crypto space. Some see it as a sign of growing adoption and renewed user interest. Others aren’t so convinced. A security researcher, Andrey Sergeenkov, has raised a less optimistic explanation, suggesting that part of this surge may be tied to address poisoning attacks taking advantage of cheaper transactions on Ethereum.
Address Poisoning Gains Traction as Fees Drop
Address poisoning is a subtle but effective tactic. Attackers send tiny transactions from wallet addresses that closely resemble legitimate ones, hoping users will later copy the wrong address from their transaction history. One small mistake, and funds are gone.
Following the Fusaka upgrade, Ethereum’s gas fees dropped by more than 60%. That change improved usability, but it also lowered the cost of running these attacks at scale. According to Sergeenkov’s findings, around 67% of newly created Ethereum accounts receive less than $1 as their first transaction. Even more telling, roughly 3.8 million accounts receive a dust transaction as their very first interaction with the network.
On the surface, this looks like explosive growth. Underneath, it may be something else entirely.
What the Charts Are Saying Right Now
From a technical perspective, Ethereum’s price action hasn’t exactly confirmed a bullish narrative. Indicators on the chart point to continued weakness. The MACD remains below zero, with the MACD line and signal line both deeply negative, suggesting bearish momentum hasn’t faded yet.
The Awesome Oscillator tells a similar story, printing a strongly negative value. Together, these signals show that while network activity is climbing, price strength is not keeping pace. That divergence raises questions about the quality of the activity being recorded.
The Real Cost of These Attacks
The damage caused by address poisoning is not theoretical. More than $740,000 has already been stolen from at least 116 known victims. The method is simple but effective. Attackers spray small amounts of stablecoins across thousands, sometimes millions, of wallets. Those fake entries then sit in transaction histories, waiting for a user to accidentally reuse the wrong address.
Beyond the financial losses, there’s another issue. This behavior inflates network activity metrics, making it harder to separate real adoption from malicious noise. Wallet creation numbers rise, transactions increase, and the network looks busier than it truly is.
A Mixed Signal for Ethereum’s Growth
None of this means Ethereum isn’t seeing genuine adoption. It clearly is, especially with staking ratios climbing and infrastructure improving. Still, the surge in activity needs to be viewed with context. Lower fees are a double-edged sword, improving access while also enabling abuse.
Ethereum’s growth story remains strong, but users should stay cautious. Rising activity doesn’t always mean healthy activity, and in this case, some of that growth may come with risks hiding just below the surface.














