Bitcoin mining is a process where miners race to verify transactions before adding them to the blockchain. More excellent hash rates indicate more significant difficulties. Automatic networks are responsible for calculating the difficulty rate in mining transactions, but certain factors may affect this rate.
Mining Difficulty: Explained
Bitcoin mining difficulty adjusts automatically to keep the time required to mine a block at about ten minutes. This depends on the amount of computing power on the network. In simple terms, if the hash rate—computing power—is higher, the difficulty is more elevated.
To ensure that every Bitcoin block is discovered within every 10 minutes, the automatic system changes the difficulty depending on many factors, such as the number of competing miners. The algorithm constantly readjusts the difficulty.
How Hashrates Comes into the Equation
Miners are trying to beat what is called the “target hash.” Higher hash rates indicate that greater computing power is needed to verify and add transactions to the blockchain. The winner is the miner who generates the code with an equal or more significant number of zeros at the front.
Bitcoin’s mining difficulty is updated every 2,016 blocks. This equates to about once every two weeks. The network determines whether the miners’ activities have collectively increased or decreased. So if it took less than ten minutes to mine a new block, the difficulty level increases. The difficulty level is reduced if it takes more than ten minutes to mine a block.
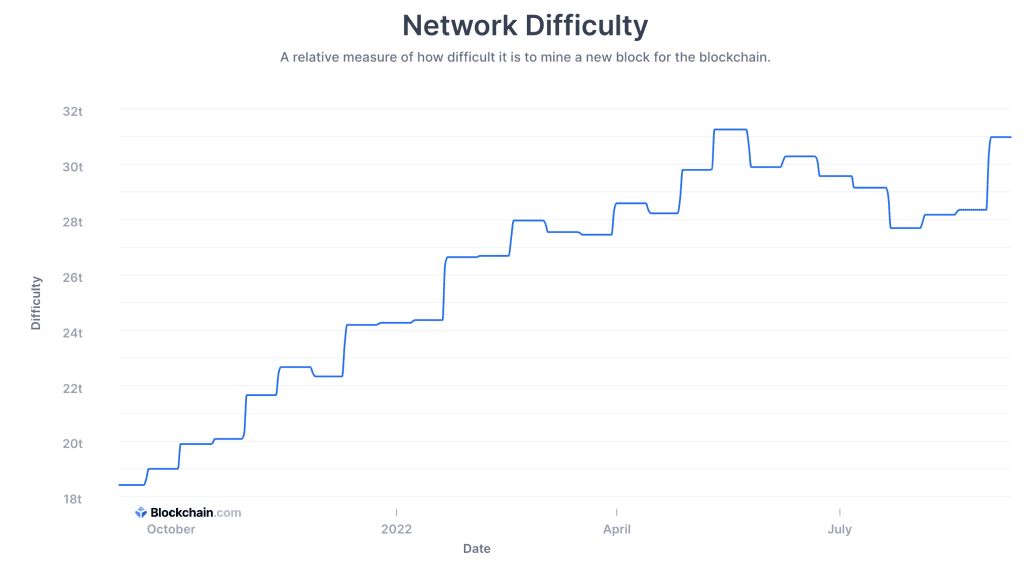
Back in July, the hash rate dropped due to miners in North America powering down due to the heat waves. This meant that mining rigs needed a lot of energy to cool down the computers due to the massive heat required to run operations.
Expected Trends in Mining Difficulty
Coindesk reports that the difficulty in mining Bitcoin is expected to increase by 9%. This is due mainly to the fact that miners in North America are “ramping up production ahead of the cooler months.”
It is predicted that this will be one of the most significant “upticks” since August 2021—characterized by miners returning to the field after the mining industry was banned in China. This was important in North America and miners since China housed about 44% of mining activity. Hashrate Index also estimates that the metric will grow by 9% to reach nearly 31 million.
Sometimes, however, the heat has the opposite effect. In Texas, mining difficulty decreased “significantly” earlier in the summer months because Bitcoin miners had turned off their machines due to the extreme heat. The power grid in Texas issued a warning to residents asking them to conserve energy.
As a result, Bitcoin miners Argo and Riot announced that they would “curtail operations.” Specifically, Argo Blockchain (@ArgoBlockchain) said in a tweet that its “Helios facility will curtail its power in Dickens County this afternoon to help conserve electricity due to the current heat wave.”
Further, Riot Blockchain’s executive vice president and chief commercial officer Chad Everett (@chadeverett) noted in a tweet that it had “curtailed all of the power to help the grid battle this extreme heat.”
New Bitcoin Mining Machines
Another factor bearing on Bitcoin’s difficulty is the new technology introduced into operations when new machines are introduced and come online. The hash rate average increases from miners plugging in new models such as Antminer S19 XP.
Regarding the introduction of new technology, Colin Harper, head of research and content at Luxor Technologies, stated that this “increase[ed] bitcoin’s seven-day average hash rate from 210 EH/s to 226 EH/s (a 7.6% increase).”
Kevin Zhang—senior vice president of mining strategy at Foundry—noted that the increase in hash rate results from heat waves and facilities coming online. Further, on this point, Ethan Vera—Chief Operating Officer at mining services firm Luxor Technologies—observed:
The post-summer network hash rate boom results from more efficient hardware delivered, summer temperatures falling in the U.S., and old-generation machines being delivered to low-cost regions.
Conclusion
Bitcoin mining is necessary for crypto transactions to be verified. Verifying transactions ensures that each block is authenticated and genuine—thus adding trust to crypto transactions. Factors such as increased heat and the introduction of new technology could have a bearing on the difficulty of mining Bitcoin.














