The polygon network, previously known as the Matic network, rebranded in early 2021 and shifted from offering a single scaling solution to a network of chains. It was founded in 2017 by Jaynti Kanani, Sandeep Nailwal, and Anurag Arjun, who joined their blockchain development and business consultancy expertise and, eventually, added Mihailo Bjelic to the co-founding team.
What is Polygon?
Polygon is a chain-agnostic network of collaborative sidechains, aspiring to become Ethereum’s ‘Internet of Blockchains .’ These sidechains are known as layer-2 solutions. They use an external, parallel network for off-chain computation, facilitating transactions away from the mainchain to improve performance. Polygon is a multiple-layer-2 infrastructure. The original Matic chain, now called the Polygon PoS side chain, is still supported and has become part of this network ecosystem.
The Polygon network
Polygon, backed by Binance and Coinbase, uses a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism and supports all the tools used on Ethereum with cheaper and faster transactions. The network has roughly $1.8 billion in total value locked (TVL), with MM Finance making up the most significant chunk.
Its most popular scaling solution is the original Matic network, i.e., the Polygon PoS chain, which runs parallel to Ethereum and relies on Ethereum for security. It processes up to 7,000 transactions per second (TPS), which is substantially superior to Ethereum’s 15 TPS, with transactions costing around $0.002.
The Polygon PoS chain is compatible with major ERC standards for fungible and non-fungible tokens, is secured by validators, and incorporates PoS checkpoints pushed to the Ethereum mainchain. The network is also EVM compatible, facilitating the deployment of smart contracts to and from Ethereum.
The network has a three-layer architecture:
- The Ethereum layer: Smart contracts on the Ethereum mainnet.
- The Heimdall layer: A set of PoS nodes monitoring the collection of staking contracts deployed on the Ethereum mainnet and committing the Polygon network checkpoints to the Ethereum mainnet
- The Bor layer: A set of block-producing Bor nodes
Last April, the Polygon PoS reached the 19,000 DApps milestones, with more than $3.4 billion transactions and 135+ million unique user addresses. It houses notable Web3 projects, such as The Sandbox and Decentral Games.
Polygon’s Native Token
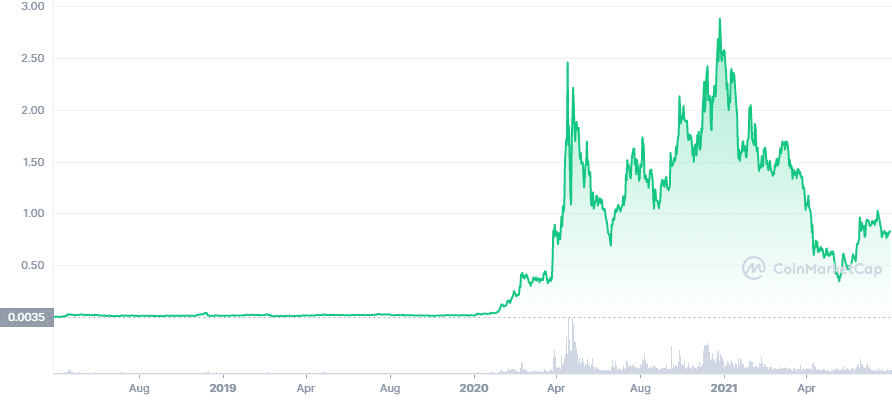
The MATIC token, the ecosystem’s native token, launched on Binance in April 2019. It is used to pay for gas fees (some of which are burned) and staking to earn rewards. The token hit an all-time high of $2.92 in December 2021 and can be bought, sold, and traded on all major exchanges. The token supply is capped at 10 billion and is currently ranked number fifteen in all cryptocurrencies by market cap. Transactions, gas fees, and more can be monitored on Polygonscan.
Other Ethereum Scaling Solutions
Polygon provides multiple solutions to Ethereum apart from the Polygon PoS chain. Some have been deployed, others using zk rollups and optimistic rollups are still in development. The live chains include:
- Polygon ID: Powered by zk technology, it focuses on providing borderless personal data ownership (e.g., birth certificates, licenses, and resident permits).
- Polygon Edge: A developer tool that facilitates the creation of new customizable blockchains tailored to the developer’s needs.
- Polygon supernets: Described by the team as Polygon Edge on steroids. They are application-specific blockchains offering developers opportunities to build a customizable environment without operational costs. These supernets can connect and communicate with each other and Ethereum. A $100 million fund is committed to developing and adopting supernets.
- Polygon Nightfall: Still in mainnet beta, it is a privacy-focused rollup developed in collaboration with Earnst and Young
Ecosystem
Polygon houses 37,000+ dApps from NFTs, games, CEXs, and DAOs. It has 135+ million unique addresses and around $4 billion MATIC staked, making it a vibrant and thriving network. New partnerships are plentiful, and some noticeable recent developments include integrating Apecoin, Terra developers’ migration, and adding MATIC to the CME reference rates. Last July, Polygon announced the first zk scaling solution fully compatible with Ethereum, considered a breakthrough in cryptographic research empowering the entire crypto space.
Ethereum’s shift to PoS this September makes Ethereum more environmentally friendly. However, it doesn’t increase its speed or transaction fees, making scaling solutions like Polygon a necessity. The Ethereum Foundation fully supports the use of layer-2s to scale while remaining decentralized and secure.














